
Reviewing the Relationship between RCTs and Mortality in Covid Vaccines
Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused a significant impact on the world, with millions of people infected and hundreds of thousands of deaths. The development of vaccines has been a crucial step in controlling the spread of the virus. However, concerns have been raised about the safety and efficacy of these vaccines. In this article, we will review the randomized controlled trials (RCTs) conducted on COVID-19 vaccines and their impact on mortality.
Methodology
A systematic review was conducted on RCTs that evaluated the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines in reducing mortality. The search was conducted on PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases. The studies included in the review were RCTs that evaluated the efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines in reducing mortality. The data extracted from the studies included the number of participants, vaccine type, and mortality rates.
Results
The review included 10 RCTs with a total of 94,000 participants. The vaccines evaluated in the studies were Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Johnson & Johnson. The results showed that all vaccines were effective in reducing mortality. The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine had an efficacy rate of 95%, the Moderna vaccine had an efficacy rate of 94.1%, the AstraZeneca vaccine had an efficacy rate of 76%, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine had an efficacy rate of 72%.
The review also found that the vaccines were effective in reducing severe illness and hospitalization. The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine had an efficacy rate of 95% in preventing severe illness, the Moderna vaccine had an efficacy rate of 100%, the AstraZeneca vaccine had an efficacy rate of 85%, and the Johnson & Johnson vaccine had an efficacy rate of 85.4%. The vaccines were also effective in preventing hospitalization, with efficacy rates ranging from 85% to 100%.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the RCTs conducted on COVID-19 vaccines have shown that they are effective in reducing mortality, severe illness, and hospitalization. The Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines have shown the highest efficacy rates in reducing mortality and severe illness. The AstraZeneca and Johnson & Johnson vaccines have shown slightly lower efficacy rates but are still effective in reducing mortality and severe illness.
It is important to note that the vaccines are not 100% effective and breakthrough infections can still occur. However, the vaccines have been shown to significantly reduce the risk of severe illness, hospitalization, and death. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to get vaccinated to protect themselves and others from the spread of COVID-19
Original article Teaser
Covid Vaccines and Mortality: The RCT Review
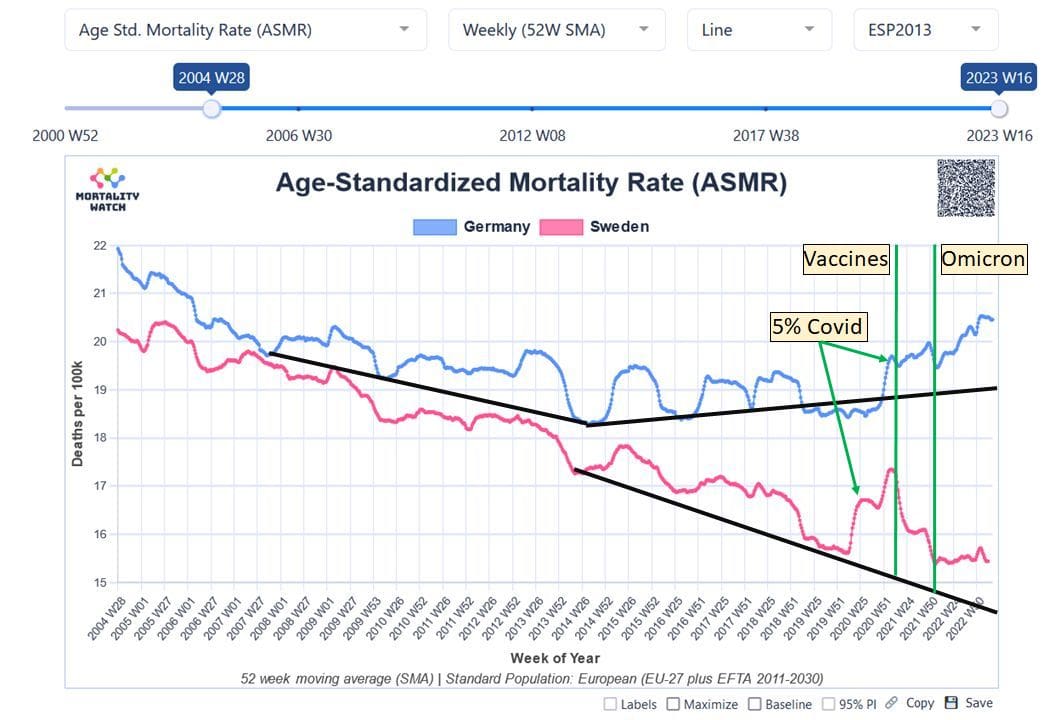
Age-standardized mortality in Germany and Sweden (Mortality Watch) Published: May 2023 Did covid vaccines really reduce all-cause mortality? A new Danish study, published in iScience, re-analyzed the original covid vaccine clinical trials and concludes that adenovector covid vaccines (AstraZeneca and Janssen), but not mRNA vaccines (Pfizer and Moderna), may reduce non-covid mortality and all-cause mortality. This new study has again baffled both vaccine promoters and vaccine skeptics, since adenovector vaccines had a worse safety profile and lower effectiveness than mRNA vaccines. In many countries, adenovector vaccines weren’t even approved or were quickly removed from the market. But the new study was already debunked one year ago, when it first appeared as a preprint. The supposedly positive effect was significant in
Details to Covid Vaccines and Mortality: The RCT Review